Imported Food Safety Management System
Manegement System
 1. Before Import 1. Before Import |
 2. Customs 2. Customs |
 3. After Import 3. After Import |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Safety Management Subject |
|
||
| Safety Management Method |
|
|
|
| Safety Management Agent |
|
|
|
- Safety management of imported foods is becoming more and more significant for food safety in Korea, as the possibility of harmful accidents exist along with concerns on proliferation of harmful substances. Therefore, MFDS is reinforcing on-site inspections for manufacturers that have high volumes of import or those that manufactured defective items. The 'Preliminary Prediction Import Inspection System (OPERA)' was also established to categorize imported foods into different grades by analyzing manufacturer and importer history as well as inspection results. Importers are now held with stronger responsibilities with higher penalties and disadvantages for intentional and recurring violations. The 「Special Act on Imported Food Safety Management」 and its sub-provisions were established to include details such as history-based inspections.
Functional Ingredient Recognition Process
| Classification | Before Enforcement | After Enforcement | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before Import | Management of overseas manufacturers through registration |
|
|
On-site inspection |
|
|
|
| Customs | Differentiated management for importer and product |
|
|
| Inspection order (Inspection order is pre-given to importer of food products with risk of hazard) |
|
|
|
| Distribution phase | Food traceability (Mandatory application) |
|
|
| Distribution management |
|
|
|
| Training order (Training order given to importers of defective products) |
|
|
|
Before Import
Business Registration
- Persons that wish to conduct business by importing and selling imported foods, by filing import declarations of imported food, etc. by proxy, by online purchasing of imported food, etc. by proxy or by storing imported food, etc. must register their business
Overseas Manufacturing Facility Registration
- Businesses that wish to import and sell imported foods or those that wish to make online purchases of imported food by proxy must register with the regional office of FDS. Moreover, businesses that wish to import overseas foods, etc. to Korea or those that establish and operate overseas manufacturing facilities must register the name, address and production item of the overseas manufacturing facility with the regional office of FDS at least seven days prior to import declaration.
※ If pre-registration is not done, import declaration will be rejected.Before Enforcement - Name of manufacturing facility, address, representative, phone number and E-mail address
- Type of business, and whether food safety management system is applied
- Type of food (processed foods, food additives, health functional foods, etc.)
- Consent for on-site inspection by visit if Minister of MFDS deems it necessary
- Confirmation that the registered information is true (If importer is applying) Confirmation that the person who established and operates the overseas manufacturing facility agreed to the registration
※ For reference, the overseas manufacturing facility written in the import declaration prior to the enforcement of the Act is irrelevant to the overseas manufacturing facility registration, and thus separate registration is required -
For change requests, only the applicant that filed the registration can make changes. If changes need to be made on matters registered by another importer, relevant details must be submitted and the person in charge of registration management (at MFDS) can make corrections based on his/her authority.
- Changes must be registered when name or address (including cases where names of administrative zones are changed) of overseas manufacturing facility is changed, or when the type of business (food or food additive, equipment and container, package manufacturing and processing, etc.) is changed
- Change to registration must be done prior to import declaration, and can be done through post-mail or online request (impfood.mfds.go.kr)
- The period of validity for the registration is two years, and it must be renewed at least seven days prior to expiration Renewal of registration can also be applied through post-mail or online request (impfood.mfds.go.kr)
On-site Inspection of Overseas Manufacturing Facility and Excellent Importer Registration System
- On-site inspection of overseas manufacturing facilities is conducted to check the safety and sanitation management status of food manufacturers in exporting countries, so as to predict and cut off possibilities of harmful damages in Korea It also aims to secure the safety of imported food by training and promoting the imported food policy in Korea and relevant food standards and specifications
※ Import can be suspended due to rejection of on-site inspection or certain inspection results. - The Excellent Importer Registration System registers businesses that check and inspect sanitation management of manufacturing facilities in exporting countries in advance as excellent importers and provide them with favorable conditions in import declaration. The system aims to encourage sellers of imported foods to voluntarily secure the safety of their products on their own.
Customs
Import Inspection
- Types of inspections on imported food can be categorized into document review, field test, laboratory test, and random sampling test
| Type of Inspection | Subject Foods | Inspection Method |
|---|---|---|
| Document Review |
|
Inspection to judge compliance of product by reviewing the submitted documents |
| Field Test |
|
Inspection to judge compliance of product by taking into consideration the product nature, conditions, taste, smell, color, labeling, packaging conditions, and history of laboratory tests. |
| Laboratory Test |
|
Inspection done with physical, chemical, or microbiological methods |
| Random Sampling Test |
|
Inspection done with physical, chemical, or microbiological methods |
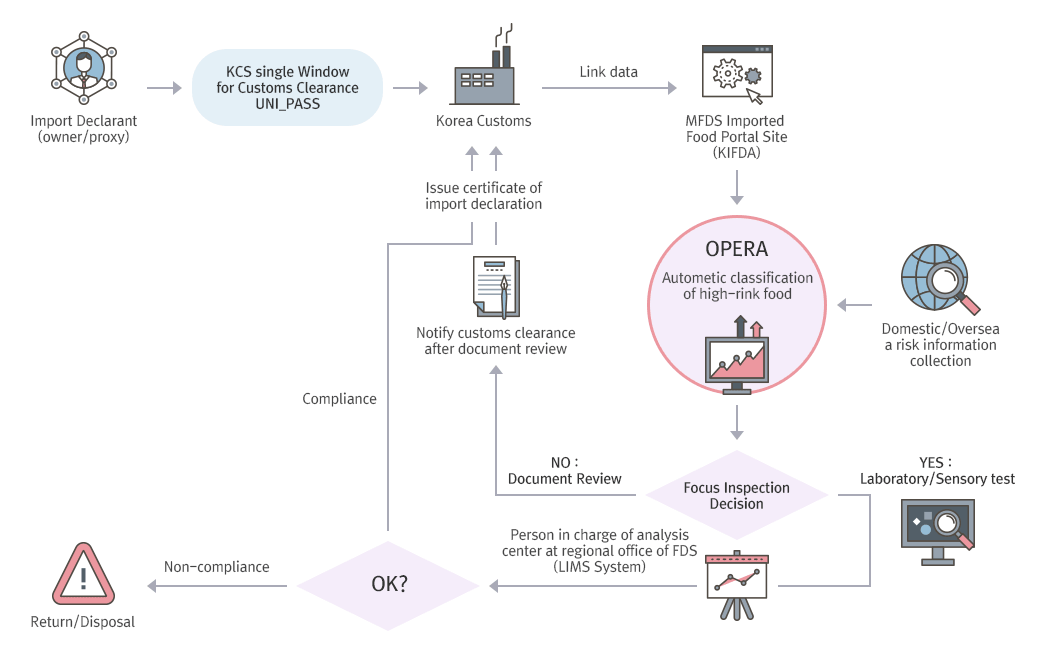
Preliminary Prediction Import Inspection System (OPERA)
- On-site inspection is strengthened for manufacturers with high import volume and those that manufactured defective products. MFDS also established and operates the OPERA (Observation & Prediction by Endless Risk Analysis) system that classifies imported food into different grades by analyzing the manufacturer and importer history along with inspection results.
- A machine automatically collects the various risk information input on the system by NFSI and the relevant imported food declaration history (including country, item, ingredients, manufacture process, importer, manufacturer, etc.), which is then analyzed by algorithms (logistic)* in real time for recommendation of certain inspection types.
Imported Food Inspection and Inspection Order System
- The inspection order system was established in 2011 for imported food products that are potentially hazardous and those with high non-compliance rates, in order to secure safety of imported foods and to raise importers' awareness on food safety
※ Document submission: Written inspection results issued by an institution specializing in food sanitation inspection (including officially certified inspection institutions overseas) must be submitted as supporting documents at time of import declaration -
Subject Food: Foods that have hazardous substances or unapproved food additives, foods with high defect rates from inspections, and foods with concern of raising harm are subject to inspection order. Specific foods subject to inspection order, inspection type and period are notified through the MFDS website or the Imported Food Information website.
Decision Criteria for Foods subject to Inspection Order - ➀ Foods where veterinary medicine, erectile-dysfunction drug or obesity drug substances are detected when it should not be included, or foods that hold the risk of such detection - Food Standards and Specifications: Article 2. Common Standards & Specifications for General Foods, Article 5. Standards and Specifications for Each Food Product; the substances under provision 11), (1), ①, and 12), (1), (2), (3)
- ➁ Foods where additives that are chemically synthesized compounds undeclared in the standards and specifications are detected, or foods that hold the risk of such detection
- ➂ Among foods that have high defect rates in import inspection, foods designated as inspection order subjects by the Minister of Food and Drug Safety
- ➃ Among other foods where potential harm was raised in and out of the country, foods designated by the Minister of Food and Drug Safety
The Hazardous Food Sales Prevention System
After Import
Collection and Inspection of Distributed Import Products
- If there is any hazardous information on the imported food products from the export country or overseas government media, the distributed import products in question are collected and inspected, and defective products are promptly recalled or seized and disposed of