Reinforcing Healthy Diets through Low-Sugar, Low-Sodium Movements
Project to Reduce Sodium Intake
- The connection between excessive sodium intake and chronic diseases such as high-blood pressure and strokes is well known, and the WHO is also emphasizing the importance of low sodium intake for maintaining a healthy living In Korea, the average daily sodium intake was 3,890mg in 2014, which was reduced by 20% from 4,878mg in 2010, but is still almost double the recommended daily average of 2,000mg. As the original target to lower average daily sodium intake to 3,900mg (20% decrease compared to 2010) by 2017 is already met, MFDS set a second reduction target to lower average daily sodium intake to 3,500mg by 2020
Nationwide Movements to Raise Consumer Awareness
- Nationwide promotion is being carried out on all fronts to raise consumer awareness on the importance of low-sodium intake, including continuous campaigns, public advertisements, idea contests for sodium reduction, ″Samsam(low-sodium)“ Food Contest, and field experience programs, along with various education and training programs held under cooperation with local governments and other Ministries such as the Ministry of Education and Ministry of National Defense
Establishing Low-Sodium Food Consumption Environment
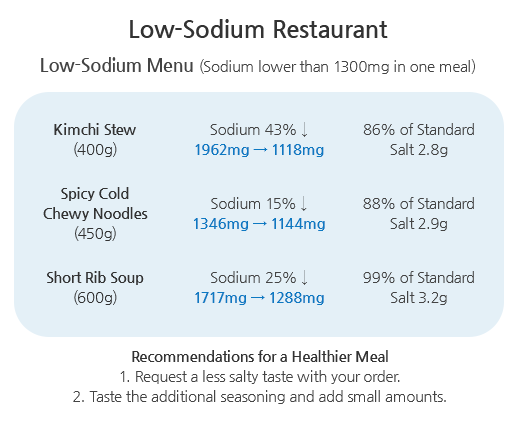
- The portion of processed foods, restaurants and meal services are continuously increasing in the overall food consumption. Therefore, various low-sodium movements have been made on these fronts, including the development of a sodium reduction guide for typically high-sodium processed foods. For restaurants and meal services, "low-sodium meal service week" was established and smaller soup bowls were supplied. From 2015, MFDS established the 「Samsam (Low-Sodium) Food Service」 system to provide less than 1,300mg of sodium for at least one meal (lunch) a day, along with the designation and management of 「Low-Sodium Restaurants」.

Signboard & Menu
Project to Reduce Sugar Intake
- In 2015, the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey analyzed people's sugar intake from 2007 to 2013 The result showed that in 2013, the average daily total sugar intake of people was 72.1g and average sugar intake from processed foods was 44.7g, which can be compared to 59.6g and 33.1g, which are the corresponding numbers of sugar intake for 2007. This indicates that sugar intake is showing a continuously increasing trend. For people between ages 3~29, sugar intake from processed foods took up more than 10% of total energy intake, and among people between ages 6~11 and ages 19~29, 46% resulted in having higher sugar intake than the amount recommended by the WHO, which is why sugar reduction projects are established and implemented.
Establishing a Safe Eat-Out Environment
Food Poisoning Prevention
- With the recent changes in people′s dietary patterns, an increasing number of the population eat out and use meal services, but at the same time, 72% of food poisoning patients come from those eating out or using meal services. In response, efforts to prevent and promptly respond to food poisoning were strengthened through pan-governmental cooperation, concentrated guidances and inspections were conducted on certain periods and facilities more vulnerable to food poisoning, and preemptive prevention measures are conducted with stronger promotion activities tailored to each food poisoning causing bacteria and season.
Structure of Pan-Governmental Cooperative Council on Food Poisoning
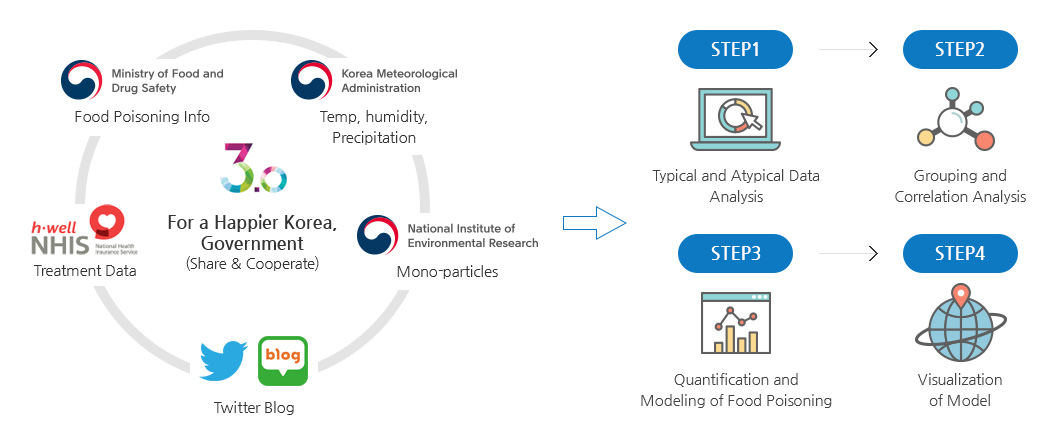
- As part of efforts in Government 3.0, the 'Food Poisoning Prediction Map' is being provided on the MFDS website to provide advanced knowledge on the potential risk level of food poisoning outbreaks, enabling preventive management. The 'Food Poisoning Prediction Map' is a connected analysis of information on MFDS food poisoning outbreaks, Korea Meteorological Administration's micro-particles, National Health Insurance Service's medical treatments and SNS data from Twitter, News, etc.
Food Poisoning Prediction Map
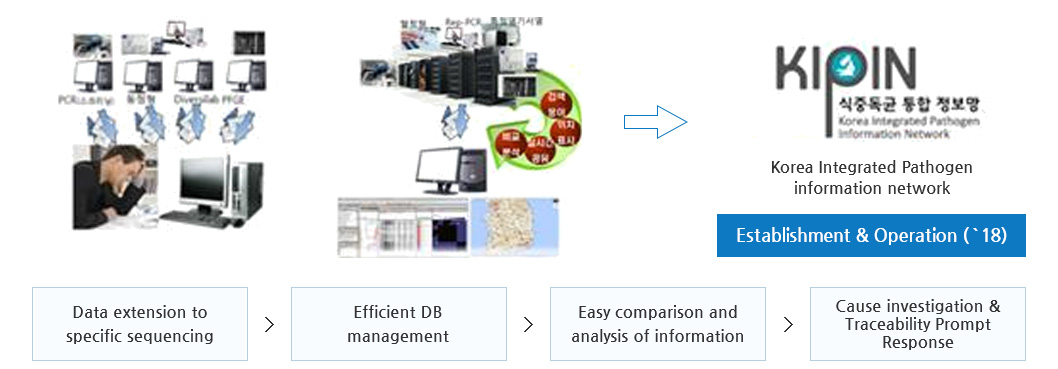
- To help clarify the cause of food poisoning, contamination monitoring has been strengthened for agricultural, livestock and marine products across all stages of production, distribution and imports. In addition, the 「Korea Integrated Pathogen Information Network (KIPIN)」 has been established and is being operated from 2015, so as to establish an integrated DB of all food poisoning causes fit to the Korean environment.
Korea Integrated Pathogen Information Network (KIPIN)
- The most effective way to prevent food poisoning is through education and promotion on prevention of food poisoning Educational programs titled 「Professional Instructor Training Course」 and 「Intensive Training for Professional Instructor on Food Poisoning Prevention」 are provided, and educational and promotional materials are also posted on the 'Food Poisoning Prevention Promotion Website (http://mfds.go.kr/fm)' for easy access and utilization.
Reinforcing Safety Control of Children′s Food
- MFDS recognized the need to have a comprehensive and systematic solution led by the government to reinforce safety of children's food, and released the ′Comprehensive Safety Measures for Children′s Food' in Feb. 2007. Based on this, the 「Special Act on Safety Management of Children′s Dietary Life」 was enacted in March 2008, and put into force in March 2009.
- According to the Special Act, zones within 200 meters radius from schools are designated and managed as 'Green Food Zones (or Children's Food Safety and Protection Zones.)' Businesses that cook and sell children's favorite foods within these zones whose facilities satisfy the sanitation standards prescribed in the 「Special Act on Safety Management of Children′s Dietary Life,」 without selling high-calorie and low-nutrition foods or high caffeine foods, are designated as 'exemplary business places selling children's favorite foods.'

- In order to encourage children to select healthy and safe foods, MFDS designated children′s foods that have higher calories and lower nutrition than as specified in certain standards and those that are likely to cause obesity or imbalance of nutrition, as ′high-calorie and low-nutrition foods′, and prohibited sales of such foods in schools or ′exemplary business place′. In addition, TV advertisements are prohibited for high-calorie and low-nutrition foods along with foods that contain high amounts of caffeine. Advertisements that lure children to make purchases are also restricted or banned.
| Type of InspecAd Classification | Restriction & Prohibition Detailstion |
|---|---|
| TV Ads | Advertisement restricted between 5 to 7PM |
| Advertising in middle of children's programs is prohibited | |
| Ads that Lure Purchases of Children | Advertisements broadcast on TV or radio or posted on the internet, that indicate free giveaways of toys or other objects other than food to lure purchases of children is prohibited |
- MFDS also operates the 'Quality Authentication System on Children's Favorite Food' that recommends manufacture, processing, distribution and sales of safe and nutritious children's favorite foods


Quality Authentication diagram on Children's Favorite Food
- In line with the 「The Special Act on Safety Management of Children′s Dietary Life」, MFDS is carrying out education and promotion activities on children's favorite food, so that children can develop the ability to put healthy and suitable dietary life into practice. The 'Nutrition and Dietary Life' textbook for elementary school(with different levels for low, mid and high-grade students) developed in 2010 has been used for steady education on food safety and nutrition since 2011. Then in 2013, food safety and nutrition education textbooks were developed for middle school and high school students and extended education based on this is being provided from 2014.
Efficient Support and Operation of the Center for Children′s Food Service Management
- For children, the future of our nation, safe food is essential for their health. This is especially important for infants and toddlers, as this is the period when children rapidly develop cognitive abilities through physical and mental growth, which lead to the development of senses on food and eating habits. Thus, it is very important for children to have foods with balanced nutrition and to develop healthy and suitable eating habits
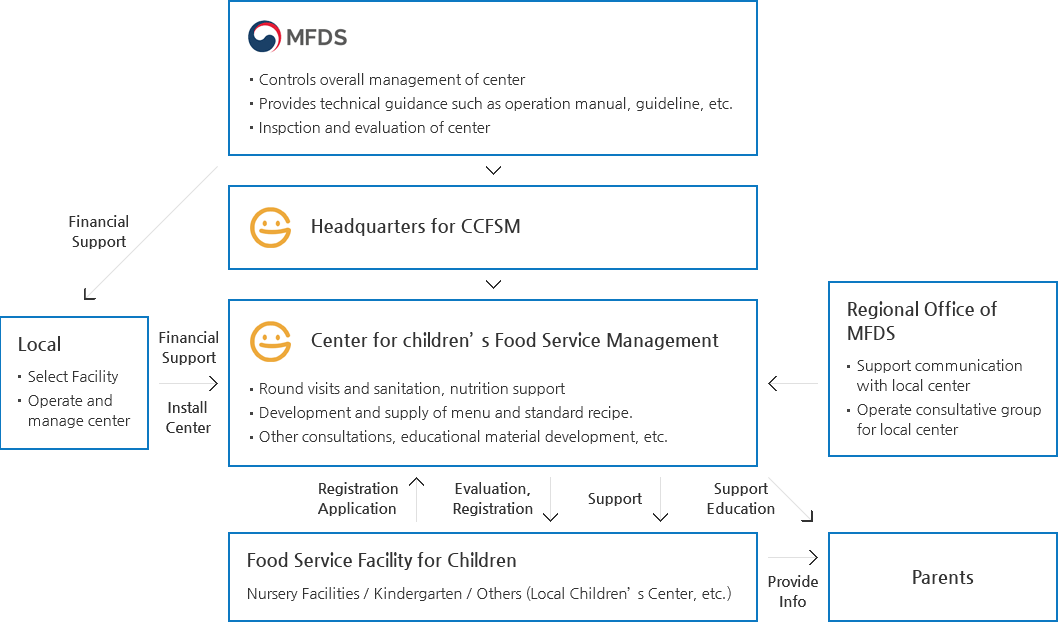
- In Korea, the number of children using nursery facilities sharply increased from 800,000 in 2002 to 1.41 million in 2014, which led parents to build higher interest in care-giving services. Thus MFDS joined hands with local governments and installed the 'Center for Children's Food Service Management' from 2011 to ensure safe management of meal services for children. To be more specific, expert dieticians from the center systematically support sanitation and nutrition management for food services provided at children's meal service facilities
Operation Structure of Center for Children′s Food Service Management