Food Safety Management System
Manegement System
 1. Manufacturing 1. Manufacturing
|
 2. Distribution 2. Distribution
|
 3. Consumption 3. Consumption
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
Safety Management
Subject |
|
|
|
|
Safety Management
Method |
|
|
|
|
Safety Management
Agent |
|
|
|
- The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety established a food safety management system to provide safer food. Domestic foods are managed through three stages: manufacturing, distribution, and consumption. In the manufacturing stage, the business operator must first submit a food manufacturing and item manufacturing report. In the manufacturing stage, self-quality inspections are conducted to ensure safety of products, and the HACCP system is applied to protect food from any hazardous risk in a preemptive manner. In the distribution stage, food products are collected and inspected to strengthen safe food distribution, and the food traceability system is operated to trace the distribution routes of harmful foods, along with the operation of the Hazardous Food Sales Prevention System. In the consumption stage, false or exaggerated advertisements are monitored and consumer food sanitation guard system is operated.
Prevention
Build Ground for
Preemptive food
Safety management
Preemptive food
Safety management
Select and Focus
Place priority on
Areas with weak
sanitation
Areas with weak
sanitation
Fast Response
Fast response to
accidents, Prevent
spread of problem
accidents, Prevent
spread of problem
Participation
and
Communication
Increase consumer
Participation and
provide information
Participation and
provide information
Manufacturing
Food Manufacturing and Item Manufacturing Report
- A person who seeks to manufacture or process foods or food additives must submit an item manufacturing report to the relevant local government prior to, or within 7 days of production initiation.
Self-Quality Inspection System
- To secure food safety prior to distribution, a business operator that manufactures or processes foods must conduct regular inspections to confirm whether the manufactured or processed foods comply with relevant standards and regulations
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) System
- HACCP, a scientific and preventive management system to secure food safety, is a system that checks, assesses, and focuses management on harmful elements that may occur from raw materials to the manufacturing, processing, cooking and distributing process of foods * HA (Hazard Analysis): Analysis of all possible biological, chemical and physical factors that lead to hazard * CCP (Critical Control Point) : Key management of the process or stage that can help prevent, eliminate, or reduce harmful elements to an acceptable level
- To strengthen the level of safety in food production and manufacturing, MFDS pushed for mandatory application of HACCP, which built legal ground in the 2002 ?Food Sanitation Act?. In August 2003, six items [processed fish products (fish cakes), frozen marine products (fish, invertebrates, flavor-treated processed products), frozen food(pizza, dumplings, noodles), ice-creams, non-pasteurized beverages, retort food products] were designated as mandatory HACCP-applied items (Kimchi cabbage added in Dec. 2006). In October 2005, the ?Hazard Analysis & Critical Control Points (Notified by MFDS)? was revised and enforced from 2006 to 2012 in multiple phases, based on the annual sales of the ′mandatory HACCP-applied items′ and the number of employees in business entities (mandatory HACCP applied to Kimchi cabbage from 2008 to 2014)
- In May 2014, the Enforcement Rule of the ?Food Sanitation Act? was amended to include 8 additional items (snacks?candies, breads?rick cakes, chocolates, fish sausages, beverages, instant foods, noodles, instant fried noodles, special purpose foods) in the list of the ′mandatory HACCP-applied items.′ Mandatory HACCP application on these items are being implemented phase-by-phase from 2014 to 2020, based on the annual sales and number of employees in 2013. (Enforcement for foods manufactured and processed in businesses recording more than KRW 10 billion in annual sales for the previous year will be completed by November 2017)
- MFDS promotes stable HACCP certification especially for children's foods including snacks and candy, along with the expansion of voluntary HACCP application. To
support smooth application of HACCP in small businesses, the Korea Institute for Food Safety Management Accreditation is providing customized technical support for
businesses that are willing or are required to apply HACCP, including technical support for HACCP operation, training and promotion free of charge ※ List of businesses
with HACCP certificates in the republic of Korea
Distribution
Collection and Inspection of Distributed Foods
- To prevent harm from food and to ensure sanitary management, food products distributed and used for sales purposes in businesses are collected and tested for compliance with standards defined by CODEX, etc. The products that do not meet the food safety standards are promptly recalled or seized and disposed of
Food Traceability
- MFDS established and operates the Food traceability system to take measures such as cause analysis, tracking, and recalls when hazards occur in foods or in health functional food products and to provide more accurate information to consumers
- MFDS revised the Enforcement Decree of ?Food Sanitation Act? and the Enforcement Decree of ?Health Functional Foods Act? to facilitate food traceability in Korea. The application of food traceability is becoming mandatory by phase for businesses that import or manufacture (process) infant and baby foods or health functional food products with annual sales exceeding a certain level and for other food product retailers operating business on stores exceeding a certain level of size The related notification (Food and Health Functional Foods Traceability Standard, etc.) was revised so that businesses are investigated and assessed every 2~3 years for follow-up management
- MFDS established and operates the 'Food Traceability Information System,' holds training sessions to encourage voluntary participation of businesses, and provides on-site training and consulting (through visits) to help stabilize and expand the system
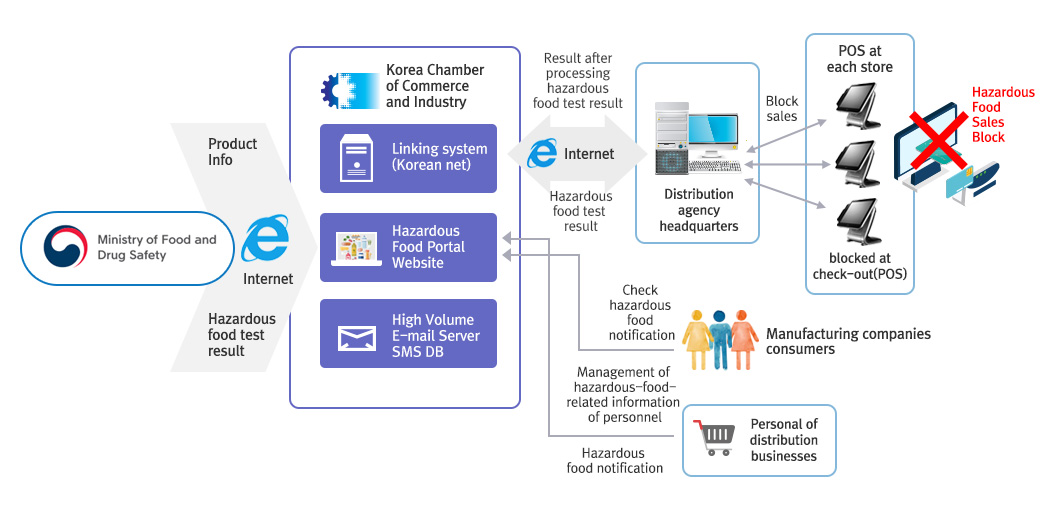
Hazardous Food Sales Prevention System
- MFDS annually collects and inspects approximately 120,000 cases of food products to secure food safety in the domestic market. On the other hand, food manufacturers also check their products' quality and safety through regular self-quality inspections. The information on defective products gathered through these tests are reported to MFDS in real-time, from approximately 85 inspection facilities nationwide. MFDS operates the ′Hazardous Food Sales Prevention System′ which enables MFDS to prevent consumers from purchasing the reported products by sending out the information on hazardous products in real-time, directly to the check-out counters in convenient stores, supermarkets and etc. HazardousFood Sales Block
- In 2009, ′Hazardous Food Sales Prevention System′ was established in the Korea Chamber of Commerce and Industry (KCCI), under the cooperation of MFDS and other relevant ministries, which was followed by a pilot project in Lotte Mart, a large distributor in Korea. As of 2015, the ′Hazardous Food Sales Prevention System′ is being installed and extended to all stores distributing and selling food products nationwide, including major supermarkets, department stores, small and medium-sized distributors, convenience stores, home shopping channels (online stores), etc.
Consumption
Monitoring of False?Exaggerated Advertising
- All advertisement media including the internet, broadcasts, newspapers, magazines and other printed materials are monitored to prevent consumer damage from false or exaggerated advertisements indicating that certain food products have therapeutic effects or making consumers confuse products as medicine
Consumer Food Sanitation Guard System
- As it is difficult to systematically monitor food service businesses with only public officers in charge of food sanitation inspection, the Consumer Food Sanitation Guard System is operated to promote consumers' active participation in food sanitation monitoring, to complement the monitoring activities of the administrative body and to secure higher transparency in food sanitation monitoring activities
Management of Food Standards and Specifications
- Food Standards and Specifications Regulations are made to provide legal ground for management of harmful elements3) in food products produced for distribution and
sales, so as to block2) the risk of harming1) the human body by consuming foods and to ensure food safety
- Businesses can secure compliance with the concerned specifications by satisfying the standards on manufacturing, processing and using, and preserving methods
- Standards and specifications for harmful elements in food products serve as a method to manage harmful elements
- Harm: The possibility of harmful factors entering the human body and causing negative impact on human health
- Block risk of harm: Managing harmful elements within an acceptable level so that even if a person is exposed to harmful elements through food consumption, there is no negative impact to human health
- Harmful elements: Chemical, biological and/or physical elements that can cause harmful impact to the human body through food products
Safety Management of Health Functional Food
Management of Standard and Criteria
- In 2004, the 「Standards and Specifications for Health Functional Food」 was established to set criteria for manufacturing·processing, production, import, distribution and preservation of health functional food products In addition, standards and specifications were established for functional ingredients and products to promote standardized distribution of health functional foods and to secure consumer safety
Functional Ingredient Recognition
- Health functional foods are products manufactured (and processed) with functional ingredients or elements useful for human health. "Functional" implies adjustment of nutrients in the human body structure or function, or those that bring useful health effects such as in physiological reaction, etc. Functional ingredients or elements can be categorized into those that are notified by the Minister of Food and Drug Safety and those that are recognized individually
Functional Ingredient
- Ingredient or element notified by the Minister of Food and Drug Safety
- Health functional food manufacturers can manufacture products fit to the predefined manufacturing standards and specifications
- Ingredient or element individually recognized by the Minister of Food and Drug Safety
- After reviewing the data submitted by business operators regarding the safety and functionality of an ingredient, the Minister of Food and Drug Safety issues an individual letter of recognition for the concerned ingredient or element The use of such ingredient or element is confined to the business operator that received the letter of recognition
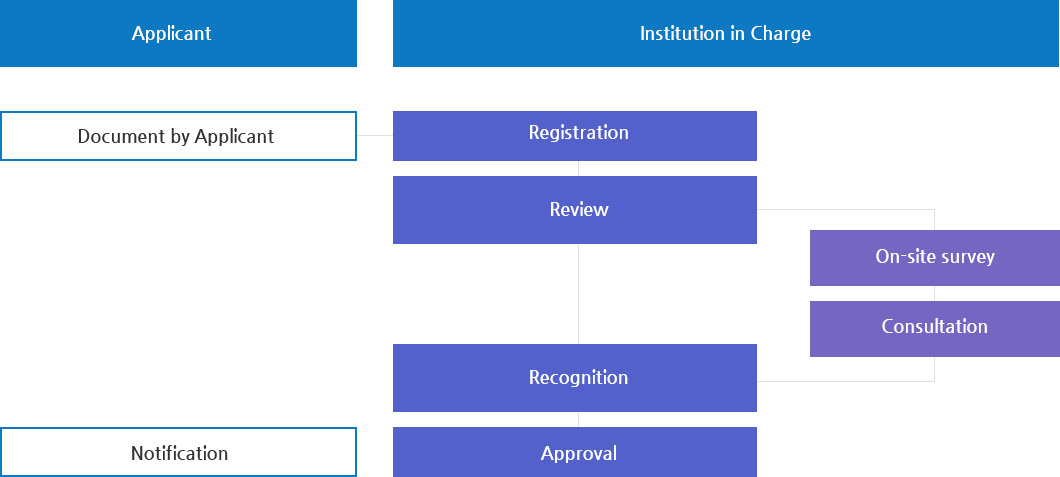
- Recognition Process
- To obtain individual recognition as a functional ingredient, the data prescribed under Article 12 and 13 of the ?Regulation on Approval of Functional ingredient and of Standard/Specification for Health Functional Food? must be submitted to MFDS. The data submitted by the business operator will be reviewed based on the standards and specifications, safety and functionality assessment standards and will be recognized as a functional ingredient under consultation with the 'Health Functional Food Deliberation Committee.'
Functional Ingredient Recognition Process
Establishing the Foundation for Manufacturing Excellent Health Functional Foods
- To secure safety and higher quality of health functional foods and to manage the manufacturing and quality of health functional foods in a more structured and systematic way, the 'Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP)' system was prepared and is currently being implemented
- At the current stage, the Excellent Health Functional Food Manufacturing Standard is not mandatory application to all Health Functional Food Manufacturers. However, if a manufacturer is recognized as applying the Excellent Health Functional Food Manufacturing Standard, then they can manufacture on commission from health functional food venture companies or health functional food distributers and sellers.
Strengthening Follow-up Management
- As various kinds of hazardous factors including new types of harmful substances and drugs such as sexual performance enhancers and depressants are increasing, to maintain the safety of health functional foods and to prevent consumers from getting harmed or injured due to illegal, false and exaggerated ads, MFDS has been carrying out strong follow-up management through collections, inspections and monitoring of the distributed health functional foods.
Collection and Analysis of Abnormal cases
- In order to manage the side effects of health functional product intake systematically and on scientific grounds, MFDS has established a "Health Functional Food Side Effect Reporting System" and has been collecting incidences of side effects and relevant information. In January 2013, MFDS unified the scattered management tasks for health functional food side-effects (which was originally Consumers Union of Korea for consumers, Korea Health Supplements Association for business operators, MFDS for expert personnels like doctors, nurses, etc.) into the National Food Safety Information Service.
- The related legal provisions were amended and the reporting criteria for business operators was strengthened from reporting at point of confirmation to point of knowledge of any side effects, which places higher priority on consumer protection Also, it was made mandatory to include 1577-2488, the number to report possible side-effects from taking health functional food, in the labeling of the package and container of health functional foods.
Mission
- Implementation policy for providing safe agriculture, livestock and fishery products
- Establishment of country's infrastructure for ensuring that people enjoy the Agriculture, livestock and fishery products
Main task
After the establishment in 2013, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) has unified safety management of Agriculture, livestock and fishery products. From production to an end-consumer, all of the steps of safety management of agriculture, livestock and fishery products is now managed and coordinated under the responsibility of MFDS in cooperation with other Ministries
Construct base for preemptive food safety management
Set priority to weak sanitation area
prompt response to an accident, block further expansion
Expand of consumer participation and actively provide information
- 1) At production stage, in order to prevent contamination of agriculture, livestock and fishery products, MFDS is cooperating with other departments like Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry and Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries so that weak areas can be intensively managed, especially producers with non-compliant record and regions that are concerns of contamination MFDS is now planning to put forth science efficiency of safety investigation at production stage by analyzing food safety information by each organization and investigation results
- 2) At manufacturing stage, a manufacturer is requested to declare manufacture of livestock and items. In order to ensure safety, self-quality inspection and HACCP system is enforced to protect food from hazards in advance. MFDS is now planning to put forth qualitative management by expanding items mandated for HACCP implementation and strengthening post-examination of HACCP certification organization, etc
- HACCP(Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) system * In order to strengthen safety of foods production and manufacturing, MFDS promoted mandatory implementation of HACCP.
| Classification | Stage | Enforcement date | Industry subject to implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy industry | 1 | Jan. 1, 2014 | |
| 2 | Jan. 1, 2015 | ||
| 3 | Jan. 1, 2016 | ||
| Processed dairy industry | 1 | Jan. 1, 2015 | |
| 2 | Jan. 1, 2016 | ||
| 3 | Jan. 1, 2017 | ||
| 4 | Jan. 1, 2018 | ||
| Processed egg industry | 1 | Dec. 1, 2016 |
Yearly total sales more than
100,000,000 won with number of employees less than 5 |
| 2 | Dec. 1, 2017 |
Yearly total sales more than
100,000,000 won with number of employees less than 5 |
SOURCE: Livestock Products Sanitation Division
- 3) At distribution and consumption stage, inspection of safety for agricultural products trading center, etc prior to distribution, collection inspection of
distributed agriculture, livestock fishery products at wholesale and domestic level, and monitoring of false/exaggerated advertisement, surveillance of livestock
sanitation, etc. will be enforced. MFDS is now planning to put forth strengthened management of distribution channel to block distribution of agricultural, livestock and
fishery products with hazardous concerns and as well as strengthened communication with consumers.
- Inspection of distributed agriculture and livestock fishery products To prevent food, etc from hazards and for sanitation, on-site visit is enforced to collect and inspect if food, etc is for sales and to check whether it is compliant to standards and specifications set by Food Code, etc or not. If the food is non-compliant as a result of collection · inspection, measures to recall or seize · discard are taken promptly
- Monitoring of false/exaggerated advertisement Monitoring of advertisement through internet, broadcast, newspaper, magazine, printed article, etc is enforced to prevent consumer damage through advertisement contents indicating that food is effective for disease treatment or advertisement contents that may be confusing with medicinal drug in advance
- Operation of consumer livestock sanitation surveillance Because it is difficult to surveil food services systematically with labor force of the officials, active participation of consumers is encouraged for surveillance of food sanitation. In order to ensure supplementation and transparency, administrative organization of surveillance through consumer food sanitation surveillance is enforced
- 4) There is a limit to ensure imported food safety just with inspection at customs clearance stage. Therefore, safety management is being expanded and implemented
to strengthen on-site safety management before exporting to Korea by mandating registration of foreign food manufacturing facilities in advance pursuant to「Special Act on
Imported Food Safety Management」, expanding facilities subject to foreign inspection and strengthening administrative matter, and implementing import sanitation evaluation
for livestock products and implementing registration of foreign facilities, etc.
Also, thorough inspection is strengthened for the substance with high potential for hazard at the customs clearance stage of imported livestock products and in order to give more consciousness of responsibility to business managers, responsibility of importer is strengthened by adjusting penalty and disadvantage of the intentional and habitual offences and fundamentally block import of non-compliant food. From now on, greater effort will be made for safety management in advance in order to block entry of hazardous food in Korea, promptly allow customs clearance of agriculture, livestock and fishery products that are safe, and conduct strengthen foreign inspection of exporting countries, etc.
Relevant Jurisdiction Law
| Law | Content | Division |
|---|---|---|
|
Livestock Products
Sanitary Control Act |
|
Agro-livestock and Fishery Products Policy Division |
|
Agricultural and Fishery
Products Quality Control Act |
|
Agricultural and Fishery Products Safety Division |
| Food Sanitation Act |
|
Foreign Inspection Division, Agricultural and Fishery Products Safety Division |
| Special Act on Imported Food Safety Management |
|
Foreign Inspection Division |
| Law regarding test and inspection on food and drug |
|
Livestock Sanitation Safety Division |
Organization chart of Agro-Livestock and Fishery Products Safety Bureau
Agro-Livestock and Fishery
Product Safety Bureau
-
Argo-Livestock and
Fishery Product Policy Division- Coordination of management plan of Sanitation and Safety Control of Agro-Livestock and Fishery Product
- Livestock Products Sanitary Control Act
- Livestock Products Labeling standard
- International cooperation on Livestock products
-
Livestock Products
Sanitation Division- Safety management on Livestock Products
- Safety Investments of Livestock Products
- HACCP Operation
- Recall of Hazard Livestock Products
- Exporting Livestock Products
-
Agricultural and Fishery
Products Safety Division- Safety management on Agricultural and Fishery Products
- Investigation and Analysis on farmland, water, etc.
- Agricultural Products Risk Assessment
- Control on Defective Agricultural and Fishery Products
- Inspection and Audit Division
- Imported Livestock, Fishery Products management
- Registration of Exporter Factory
- Investigation of cause on Import Inconsistence